男性,26岁。右上胸部外伤急诊患者。平片发现右上纵膈异常而行ct和dsa检查。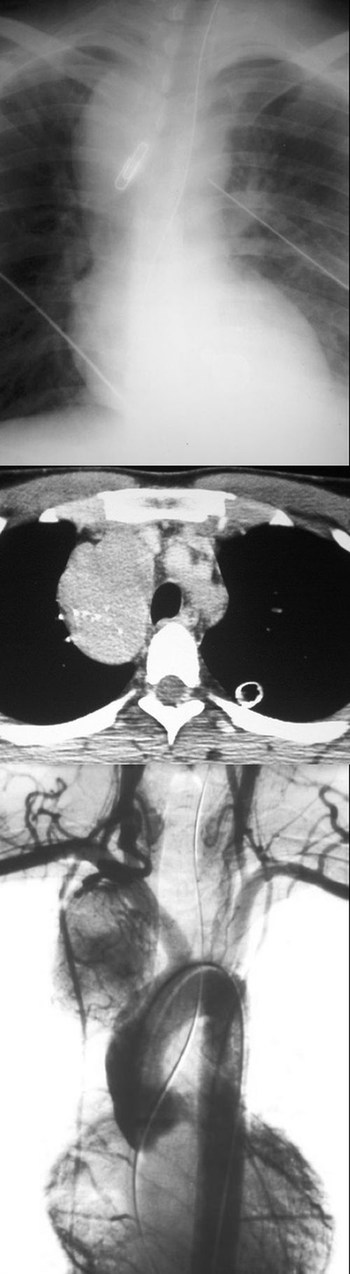 dyqct发言:占位性病变 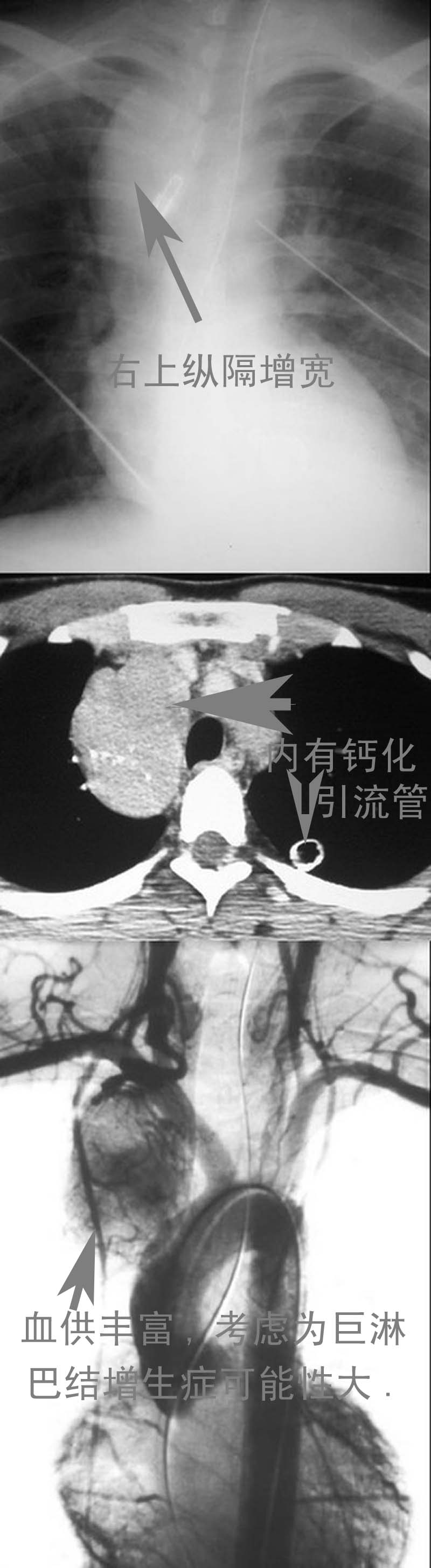 卜一发言:定位:中纵隔. 特征:类圆形,边界清楚,占位效应明显,富血供. 定性:首先考虑_淋巴瘤. 建议:增强. 结果: 局限性巨淋巴结增生(透明血管型)。 ]   pp点评: 请看由zhangyong版主发布的腹膜后局限性巨淋巴结增生病例: v0090:http://www.radinet.com.cn/forum_view.asp?forum_id=33&view_id=15905 病例①: age/sex: 58/m chief complaints: extremity weakness, sensory change, and skin lesion 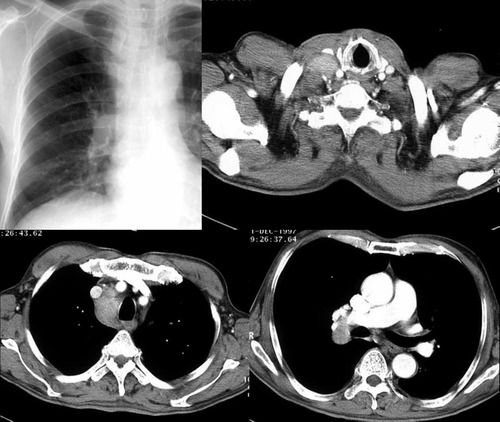 病例②: age / sex:40 / m chief complaint:routine check-up . history of operation due to mediastinal mass ten years before.  病例③: age / sex:23 / male chief complaint: recurrent lymphadenopathy in the preauricular, elbow and bilateral inguinal areas diagnosis: multicentric castleman\'s disease with lung involvement (lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis) 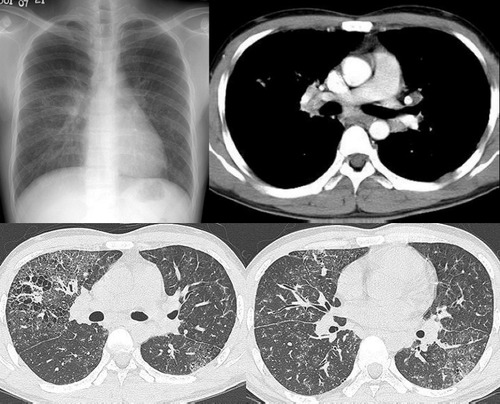 病例④: age / sex:44 / female chief complaint: asymptomatic, chest radiograph abnormality 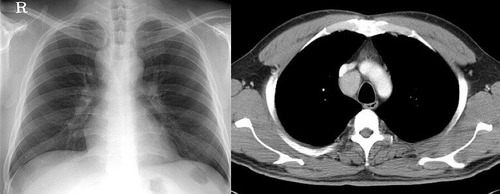 病例⑤: age / sex:21 / male chief complaint:incidental detected mass at left hilum  病例⑥: age / sex:31 / f chief complaint:incidental cxr abnormality on routine health exam  病例⑦: age / sex:40 / m chief complaint: incidental abnormality on chest radiograph  病例⑧: 39 / m; chest discomfort 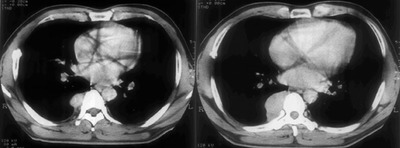 病例⑨: 40 / f, incidental mass on croutine check  病例⑩: age / sex:28 / f chief complaint: left hilar abnormality on routine chest radiograph 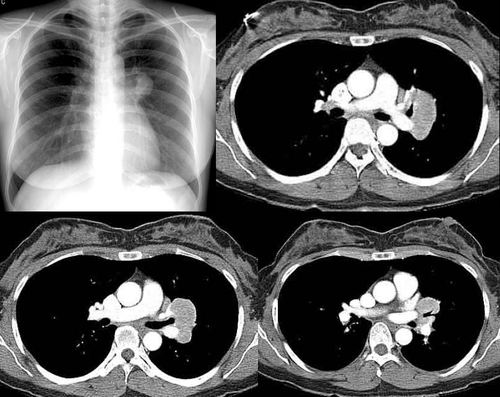 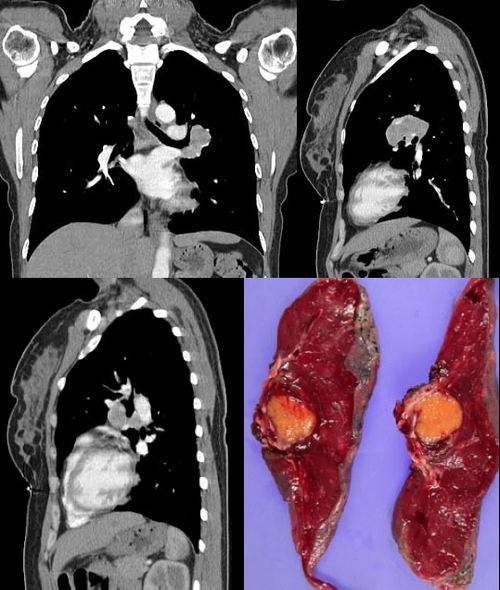 pp点评: brief review castleman disease, also known as angiofollicular hyperplasia or giant lymph node hyperplasia, is a rare disorder of lymphoid tissue. unclear etiology and pathogenesis. this disease may occur anywhere along the lymphatic chain but it is most commonly found as a solitary mass in the mediastinum. two distinct histologic patterns of castleman disease have been described, including the hyaline-vascular type, accounting for 90% of cases, and the remainder of cases as the plasma cell type, which is often associated with constitutional symptoms. three patterns have been reported on ct or mri, including a solitary noninvasive mass (50%), a dominant infiltrative mass with associated lymphadenopathy (40%), and a matted lymphadenopathy without a dominant mass (10%) in castleman disease, ct with contrast material usually shows a dense uniform enhancement. dynamic ct demonstrates early rapid enhancement and washout in the delayed phase, which are considered as typical imaging characteristics that help to differentiate this disease from other mediastinal tumors such as lymphoma etc. furthermore, peripheral hypervascularity is a characteristic finding on power doppler ultrasonography. a punctate or arborizing pattern of calcification may be seen. some recent studies have reported a considerable number of cases showing heterogeneous attenuation. meador and mclarney reported that tumors greater than 5 cm in diameter generally demonstrate heterogeneous enhancement. in several studies, a focal low attenuation area within the mass showing delayed enhancement on dynamic ct or mri, was pathologically proven to be central stellate fibrosis interspersed within the mass. an mri study has been reported to be useful for the evaluation of peripheral or tumoral hypervascularity and the relationship with adjacent vascular structures, because vascular structures appear signal void with high contrast to the mass. treatment of castleman disease is as follows. surgical resection is recommended for patients with the unicentric variant of cd because surgical removal of a unicentric mass of hyaline-vascular or hyaline-vascular/plasma cell type is curative. but if it is not possible, partial resection, radiotherapy, or observation alone may be helpful instead of excessively aggressivie therapy. patients with multicentric disease, either hyaline-vascular or plasma cell type, do not benefit from surgical management and should be candidates for multimodality therapy, the nature of which has yet to be defined.. 原贴地址:http://www.radinet.com.cn/forum_view.asp?forum_id=33&view_id=18620 |